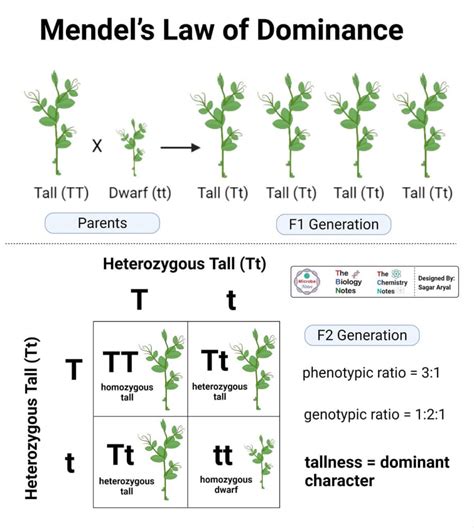
The concept of complete dominance in genetic traits is a fundamental principle in genetics, referring to a specific type of gene interaction where one allele (a variant of a gene) completely masks the effect of another allele. This phenomenon is crucial in understanding how genetic traits are inherited and expressed in organisms. Complete dominance is one of the basic principles of Mendelian genetics, named after Gregor Mendel, who first described these laws of inheritance in the 19th century. To grasp the concept of complete dominance, it's essential to understand the basics of alleles and genotypes.
Genetic Basis of Complete Dominance
In genetics, each gene comes in different versions called alleles. For a particular gene, an individual can have two copies (one from each parent) that are the same (homozygous) or different (heterozygous). When we talk about complete dominance, we’re referring to a situation where one allele (let’s call it “A”) will always be expressed if an individual has one or two copies of it (AA or Aa), and the other allele (“a”) has no effect on the trait when paired with “A”. The allele that is expressed is called the dominant allele, and the one that is masked is called the recessive allele.
Examples of Complete Dominance
A classic example of complete dominance is the trait for flower color in pea plants, one of Mendel’s original studies. In pea plants, the gene for purple flowers (P) is dominant over the gene for white flowers (p). A plant with the genotype PP or Pp will have purple flowers because the dominant “P” allele masks the effect of the recessive “p” allele. Only plants with the genotype pp will express the recessive trait, having white flowers. This is a clear demonstration of complete dominance, where the presence of one dominant allele is enough to determine the trait’s expression.
| Genotype | Phenotype |
|---|---|
| PP | Purple flowers |
| Pp | Purple flowers |
| pp | White flowers |
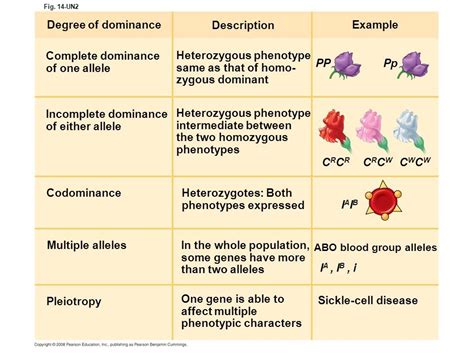
Implications of Complete Dominance
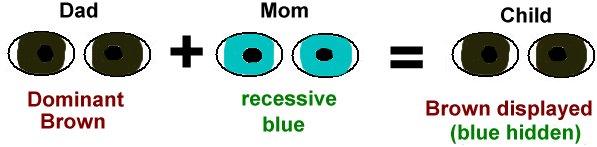
Complete dominance has significant implications in genetics and breeding. It helps in understanding how certain traits are passed down through generations and can be used to predict the probability of offspring expressing certain traits. This knowledge is crucial in agriculture for cultivating crops with desirable traits, such as disease resistance or improved yield, and in medicine for understanding genetic diseases and developing targeted treatments.
Limitations and Complexities
While complete dominance provides a straightforward model for understanding some genetic traits, not all traits follow this simple pattern. Many traits are influenced by multiple genes (polygenic traits) or show incomplete dominance, where the effect of the two alleles combines to produce a phenotype that is different from either of the parental phenotypes. Additionally, environmental factors can influence the expression of genetic traits, adding another layer of complexity to the study of genetics.
Key Points
- Complete dominance occurs when one allele completely masks the effect of another allele.
- The dominant allele will always be expressed if an individual has one or two copies of it.
- Understanding complete dominance is crucial for predicting the expression of traits in offspring.
- This principle has significant implications in agriculture and medicine for cultivating desirable traits and understanding genetic diseases.
- Not all traits follow the pattern of complete dominance; many are influenced by multiple genes or environmental factors.
In conclusion, complete dominance is a fundamental concept in genetics that helps explain how certain traits are inherited. Its implications are far-reaching, from agricultural breeding to medical genetics. However, it's also important to recognize the limitations and complexities of genetic inheritance, as many traits do not follow the simple model of complete dominance. Continued research and understanding of genetics will provide deeper insights into the complex interactions between genes and environment that shape the traits of organisms.
What is the difference between a dominant and recessive allele?
+A dominant allele will be expressed if an individual has one or two copies of it, while a recessive allele will only be expressed if an individual has two copies of it, with no copies of the dominant allele present.
Can complete dominance be observed in human traits?
+Yes, complete dominance can be observed in some human traits, such as the ability to roll one’s tongue, which is determined by a dominant allele. However, many human traits are polygenic, meaning they are influenced by multiple genes, making the expression of traits more complex.
How is complete dominance used in agriculture?
+Complete dominance is used in agriculture to breed crops with desirable traits such as disease resistance or improved yield. By understanding how these traits are inherited, farmers can selectively breed plants that express the desired dominant allele, leading to more resilient and productive crops.