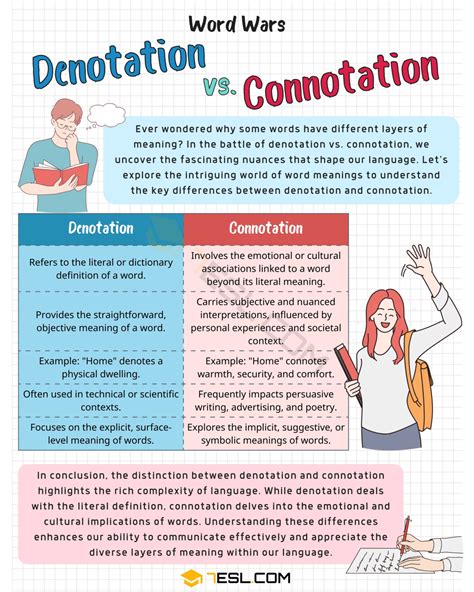
The study of language and meaning has long been a cornerstone of linguistic inquiry, with two fundamental concepts at its core: connotation and denotation. These terms, often used in tandem, delve into the complexities of word meaning, shedding light on how language influences our perceptions and understanding of the world. The distinction between connotation and denotation is crucial for effective communication, as it highlights the dual nature of language—where words can have both a literal, objective meaning and a subjective, interpretive one.
Denotation refers to the literal or dictionary definition of a word, which is often considered its primary or objective meaning. It is the meaning that is commonly agreed upon by speakers of a language and is usually the first definition provided in dictionaries. For instance, the denotation of the word "dog" is a domesticated carnivorous mammal that is often kept as a pet. This meaning is straightforward and does not vary significantly across different contexts or cultures, making it a stable reference point for communication.
Connotation, on the other hand, encompasses the emotional, cultural, or personal associations that a word evokes beyond its literal meaning. These associations can be positive, negative, or neutral and are influenced by an individual's experiences, cultural background, and the context in which the word is used. Returning to the example of "dog," while its denotation is clear, its connotation can vary. For some, "dog" might connote loyalty and companionship, evoking feelings of warmth and affection. For others, it might connote fear or nuisance, depending on their personal experiences or cultural perceptions.
Key Points
- Denotation is the literal or dictionary definition of a word, representing its objective meaning.
- Connotation refers to the subjective, emotional, or cultural associations a word carries beyond its literal meaning.
- The distinction between denotation and connotation is crucial for understanding the nuances of language and effective communication.
- Context plays a significant role in determining the connotation of a word, as the same word can have different connotations in different situations.
- Personal experiences, cultural background, and historical context can influence the connotation of words, making language a dynamic and complex system.
Understanding Connotation and Denotation in Language Use

The interplay between connotation and denotation is a vital aspect of language use, as it affects how messages are conveyed and interpreted. In everyday communication, words are rarely used in isolation from their connotations. Instead, the choice of words is often influenced by the desired connotation, reflecting the speaker’s or writer’s intent to evoke specific emotions or attitudes in their audience. For instance, in political discourse, the terms “reform” and “revolution” both denote change, but they connote different levels of radicalness and approach to achieving that change.
The Impact of Context on Connotation
Context is a critical factor in determining the connotation of a word. The same word can have different connotations in different contexts, highlighting the dynamic nature of language. For example, the word “home” generally has a positive connotation, suggesting warmth, comfort, and safety. However, in the context of “homeless,” the connotation shifts, emphasizing a lack of these very qualities. This context-dependent nature of connotation underscores the importance of considering the setting in which language is used to fully grasp its meaning.
| Term | Denotation | Connotation |
|---|---|---|
| Home | A person's permanent or usual residence | Warmth, comfort, safety (generally positive) |
| Homeless | Without a home or permanent residence | Lack of safety, comfort, and stability (negative) |
Practical Applications of Understanding Connotation and Denotation
The practical applications of understanding the difference between connotation and denotation are far-reaching. In marketing, for instance, the choice of words with the right connotation can make a significant difference in how a product or service is perceived by potential customers. A company might choose to use words that connote luxury, sustainability, or innovation, depending on its brand identity and target audience. Similarly, in legal contexts, the connotation of words can influence the interpretation of laws and contracts, emphasizing the need for precise language to avoid misunderstandings.
Cultural and Historical Considerations
Cultural and historical contexts also play a crucial role in shaping the connotations of words. What might be considered a positive connotation in one culture could be viewed negatively in another. Furthermore, historical events can alter the connotations of words over time. For example, the term “quarantine” originally denoted a period of 40 days, derived from the Italian words “quaranta” meaning 40, during which ships arriving in Venice were required to anchor offshore before landing to ensure they did not bring disease ashore. The connotation of “quarantine” has evolved to connote isolation, often in the context of public health measures, reflecting societal responses to disease outbreaks.
In conclusion, the concepts of connotation and denotation are fundamental to understanding the complexities of language and its role in shaping our perceptions and interactions. By recognizing the distinction between the literal meaning of words (denotation) and their broader, subjective associations (connotation), we can navigate the nuances of communication more effectively. This understanding is not only essential for personal and professional communication but also critical in various fields where the precise use of language can have significant consequences.
What is the primary difference between connotation and denotation?
+The primary difference between connotation and denotation is that denotation refers to the literal or dictionary definition of a word, while connotation refers to the emotional, cultural, or personal associations that a word evokes beyond its literal meaning.
How does context influence the connotation of a word?
+Context plays a significant role in determining the connotation of a word. The same word can have different connotations in different contexts, reflecting the dynamic and nuanced nature of language. Factors such as cultural background, personal experiences, and the specific situation in which the word is used can all impact its connotation.
Why is understanding connotation and denotation important in practical applications?
+Understanding the difference between connotation and denotation is crucial for effective communication, as it allows individuals to choose words that convey the intended meaning and avoid misunderstandings. This is particularly important in fields such as marketing, law, and international relations, where the precise use of language can have significant consequences.


