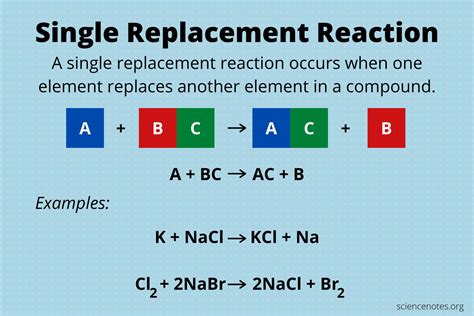
A single replacement chemical reaction, also known as a single displacement reaction, is a type of chemical reaction where one element replaces another element in a compound. This type of reaction is characterized by the exchange of one element for another, resulting in the formation of a new compound and a new element. The general equation for a single replacement reaction is: A + BC → AC + B, where A is the element that replaces element B in the compound BC.
Understanding Single Replacement Reactions

To understand single replacement reactions, it’s essential to consider the reactivity of the elements involved. Elements that are more reactive tend to replace less reactive elements in compounds. The reactivity series, also known as the activity series, is a list of elements in order of their reactivity, with the most reactive elements at the top. This series can be used to predict whether a single replacement reaction will occur.
Example of a Single Replacement Reaction
A common example of a single replacement reaction is the reaction between zinc (Zn) and copper sulfate (CuSO4). In this reaction, zinc replaces copper in the compound copper sulfate, resulting in the formation of zinc sulfate (ZnSO4) and copper (Cu). The equation for this reaction is: Zn + CuSO4 → ZnSO4 + Cu. This reaction is a classic example of a single replacement reaction, where a more reactive element (zinc) replaces a less reactive element (copper) in a compound.
| Reactant | Product |
|---|---|
| Zinc (Zn) | Copper (Cu) |
| Copper Sulfate (CuSO4) | Zinc Sulfate (ZnSO4) |

Key Characteristics of Single Replacement Reactions

Single replacement reactions have several key characteristics that distinguish them from other types of chemical reactions. These characteristics include: the replacement of one element for another, the formation of a new compound and a new element, and the prediction of reactivity based on the reactivity series. Understanding these characteristics is essential for predicting and analyzing single replacement reactions.
Prediction of Single Replacement Reactions
Predicting whether a single replacement reaction will occur requires an understanding of the reactivity of the elements involved. By using the reactivity series, it’s possible to predict whether a more reactive element will replace a less reactive element in a compound. This prediction is based on the relative reactivity of the elements, with more reactive elements tending to replace less reactive elements.
Key Points
- Single replacement reactions involve the replacement of one element for another in a compound.
- The general equation for a single replacement reaction is: A + BC → AC + B.
- The reactivity series can be used to predict whether a single replacement reaction will occur.
- Single replacement reactions have several key characteristics, including the replacement of one element for another and the formation of a new compound and a new element.
- Predicting single replacement reactions requires an understanding of the reactivity of the elements involved.
Real-World Applications of Single Replacement Reactions
Single replacement reactions have several real-world applications, including the extraction of metals from their ores and the production of chemicals. For example, the reaction between zinc and copper sulfate is used to extract copper from copper ore. Additionally, single replacement reactions are used in the production of chemicals, such as the production of zinc sulfate, which is used in the manufacture of rayon and other textiles.
Industrial Applications of Single Replacement Reactions
Single replacement reactions are used in various industrial processes, including metallurgy, chemical production, and water treatment. For example, the reaction between zinc and copper sulfate is used in the extraction of copper from copper ore, while the reaction between sodium and chlorine is used in the production of sodium chloride (table salt). Understanding single replacement reactions is essential for optimizing these industrial processes and improving efficiency.
What is a single replacement reaction?
+A single replacement reaction is a type of chemical reaction where one element replaces another element in a compound, resulting in the formation of a new compound and a new element.
How can single replacement reactions be predicted?
+Single replacement reactions can be predicted by using the reactivity series, which lists elements in order of their reactivity. More reactive elements tend to replace less reactive elements in compounds.
What are some real-world applications of single replacement reactions?
+Single replacement reactions have several real-world applications, including the extraction of metals from their ores, the production of chemicals, and water treatment. For example, the reaction between zinc and copper sulfate is used to extract copper from copper ore.