The concept of percent yield is crucial in chemistry, particularly in the context of chemical reactions. It is a measure of the efficiency of a reaction, indicating how much of the desired product is actually obtained compared to the theoretical maximum yield. Calculating percent yield is essential for chemists to evaluate the success of their experiments, identify potential issues, and optimize reaction conditions. In this article, we will delve into the details of calculating percent yield, exploring the theoretical background, the formula, and practical examples.
Key Points
- Percent yield is a measure of the efficiency of a chemical reaction.
- The theoretical yield is calculated based on the stoichiometry of the reaction.
- Actual yield is the amount of product obtained in the experiment.
- The percent yield formula is: (Actual Yield / Theoretical Yield) * 100.
- Percent yield can be used to evaluate the success of a reaction and identify areas for improvement.
Understanding Theoretical Yield

Theoretical yield, also known as the stoichiometric yield, is the maximum amount of product that can be obtained from a given amount of reactants, based on the balanced chemical equation. It assumes that the reaction goes to completion without any losses or side reactions. To calculate the theoretical yield, one needs to know the limiting reactant, which is the reactant that will be completely consumed first and thus determines the maximum amount of product that can be formed.
Calculating Theoretical Yield
The calculation of theoretical yield involves several steps. First, one must balance the chemical equation to determine the mole ratios between reactants and products. Then, the number of moles of the limiting reactant is calculated, usually by using its mass and molar mass. Finally, the moles of the limiting reactant are converted into moles of product using the mole ratio from the balanced equation, and then into mass using the molar mass of the product.
| Reactant/Product | Moles | Molar Mass (g/mol) | Mass (g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Limiting Reactant | Calculated Moles | Known Molar Mass | Given Mass |
| Product | Calculated Moles from Limiting Reactant | Known Molar Mass of Product | Theoretical Yield |

Calculating Actual Yield
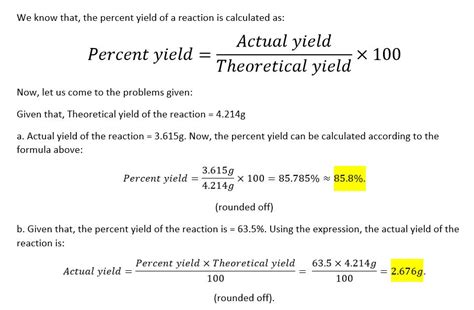
Actual yield, on the other hand, is the amount of product that is actually obtained from the reaction. This can be measured directly after the reaction is complete and the product is isolated and purified. The actual yield is typically less than the theoretical yield due to various losses and inefficiencies during the reaction and product isolation process, such as side reactions, incomplete reactions, and purification losses.
Measuring Actual Yield
Measuring the actual yield involves quantifying the amount of product obtained. This can be done using various methods such as weighing the product, using chromatography to determine the purity and amount of product, or through other analytical techniques depending on the nature of the product and the reaction.
Calculating Percent Yield
The percent yield of a reaction is calculated by dividing the actual yield by the theoretical yield and then multiplying by 100. This gives a percentage that indicates how efficient the reaction was in producing the desired product. A percent yield of 100% indicates that the reaction was perfectly efficient, with no losses or side reactions, while a lower percent yield indicates inefficiencies or losses during the reaction.
The formula for calculating percent yield is:
Percent Yield = (Actual Yield / Theoretical Yield) * 100
Example: If the theoretical yield of a product is 10 grams and the actual yield obtained is 8 grams, the percent yield would be (8 / 10) * 100 = 80%.
What factors can affect the percent yield of a reaction?
+Several factors can affect the percent yield, including reaction conditions (temperature, pressure, solvent), the presence of impurities, the efficiency of the purification process, and the stoichiometry of the reaction.
How can percent yield be improved?
+Improving percent yield involves optimizing reaction conditions, ensuring high purity of reactants, optimizing the stoichiometry of the reaction, and improving the efficiency of product isolation and purification techniques.
What is the significance of calculating percent yield in chemical reactions?
+Calculating percent yield is significant because it provides a measure of the efficiency and effectiveness of a chemical reaction. It helps in identifying areas for improvement, optimizing reaction conditions, and scaling up reactions for industrial applications.
In conclusion, calculating percent yield is a fundamental aspect of chemical reactions, providing valuable insights into the efficiency and effectiveness of the reaction process. By understanding how to calculate theoretical yield, actual yield, and percent yield, chemists can evaluate the success of their experiments, identify potential issues, and optimize reaction conditions to achieve higher yields and better product quality.



