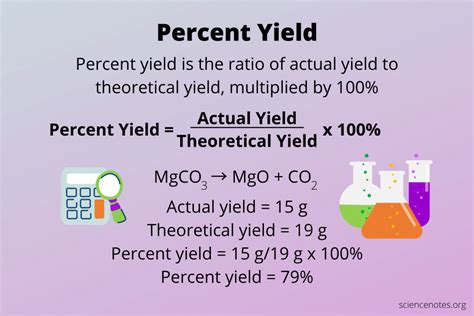
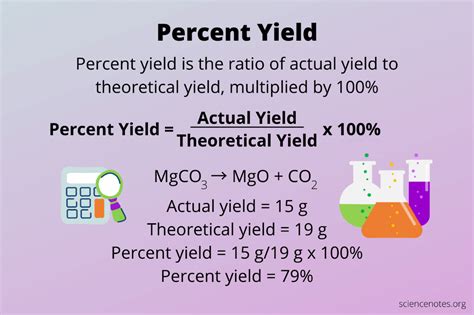
Computing percent yield is a crucial step in various chemical reactions, as it helps determine the efficiency and productivity of a process. Percent yield, also known as percentage yield, is the ratio of the actual yield of a product to the theoretical yield, expressed as a percentage. In this article, we will delve into the concept of percent yield, its importance, and provide a step-by-step guide on how to compute it.
Key Points
- Understanding the concept of percent yield and its significance in chemical reactions
- Learning the formula to calculate percent yield: (actual yield / theoretical yield) x 100
- Identifying the factors that affect percent yield, such as reaction conditions and reagent purity
- Applying the concept of percent yield to real-world scenarios, including industrial processes and laboratory experiments
- Recognizing the importance of optimizing reaction conditions to maximize percent yield
What is Percent Yield?

Percent yield is a measure of the efficiency of a chemical reaction, representing the percentage of the theoretical yield that is actually obtained. The theoretical yield is the maximum amount of product that can be formed based on the stoichiometry of the reaction, while the actual yield is the amount of product that is actually obtained. By calculating the percent yield, chemists can evaluate the success of a reaction and identify areas for improvement.
Importance of Percent Yield
The importance of percent yield lies in its ability to provide a quantitative measure of reaction efficiency. A high percent yield indicates that the reaction is efficient, while a low percent yield suggests that the reaction is not optimized. Percent yield is crucial in various fields, including pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and materials science, where the production of high-purity products is essential.
How to Compute Percent Yield

To compute percent yield, you need to know the actual yield and the theoretical yield of the product. The formula to calculate percent yield is:
Percent Yield = (Actual Yield / Theoretical Yield) x 100
Where:
- Actual Yield is the amount of product obtained in the reaction
- Theoretical Yield is the maximum amount of product that can be formed based on the stoichiometry of the reaction
For example, suppose you are synthesizing a compound with a theoretical yield of 10 grams, but you only obtain 8 grams of the product. To calculate the percent yield, you would use the following formula:
Percent Yield = (8 g / 10 g) x 100 = 80%
This means that the reaction has a percent yield of 80%, indicating that 80% of the theoretical yield was obtained.
Factors Affecting Percent Yield
Several factors can affect the percent yield of a reaction, including:
- Reaction conditions, such as temperature, pressure, and solvent
- Reagent purity and concentration
- Catalyst activity and selectivity
- Reaction time and kinetics
By optimizing these factors, chemists can improve the percent yield of a reaction, resulting in higher productivity and efficiency.
| Reaction Condition | Effect on Percent Yield |
|---|---|
| Temperature | High temperatures can increase reaction rates, but may also lead to side reactions and decreased percent yield |
| Pressure | High pressures can increase reaction rates, but may also lead to equipment damage and decreased percent yield |
| Solvent | The choice of solvent can affect reaction rates, selectivity, and percent yield |
Real-World Applications of Percent Yield
Percent yield has numerous real-world applications in various fields, including:
- Pharmaceuticals: Percent yield is crucial in the production of high-purity pharmaceuticals, where even small variations in yield can affect product quality and efficacy
- Agrochemicals: Percent yield is essential in the production of agrochemicals, where high yields are necessary to ensure crop protection and food security
- Materials Science: Percent yield is important in the production of advanced materials, where high yields are necessary to ensure material properties and performance
Optimizing Reaction Conditions to Maximize Percent Yield
To maximize percent yield, chemists can optimize reaction conditions, such as temperature, pressure, and solvent. Additionally, the use of catalysts and additives can improve reaction rates and selectivity, leading to higher percent yields.
In conclusion, computing percent yield is a critical step in chemical synthesis, as it provides a quantitative measure of reaction efficiency. By understanding the factors that affect percent yield and optimizing reaction conditions, chemists can improve the productivity and efficiency of chemical reactions, leading to cost savings and environmental benefits.
What is the formula to calculate percent yield?
+The formula to calculate percent yield is: (Actual Yield / Theoretical Yield) x 100
What factors can affect percent yield?
+Several factors can affect percent yield, including reaction conditions, reagent purity and concentration, catalyst activity and selectivity, and reaction time and kinetics
Why is percent yield important in chemical synthesis?
+Percent yield is important in chemical synthesis because it provides a quantitative measure of reaction efficiency, allowing chemists to evaluate the success of a reaction and identify areas for improvement