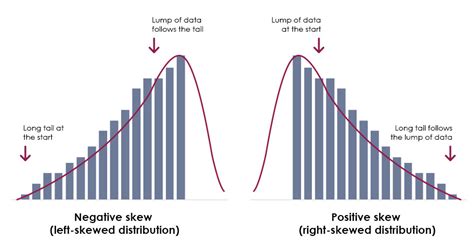
A left skewed distribution, also known as a negatively skewed distribution, is a type of probability distribution where the majority of the data points are concentrated on the right side of the distribution, with a longer tail on the left side. This type of distribution is commonly observed in real-world data, particularly in fields such as economics, finance, and social sciences. In a left skewed distribution, the mean is typically less than the median, which is less than the mode. This is in contrast to a right skewed distribution, where the mean is greater than the median, which is greater than the mode.
Left skewed distributions are often characterized by a small number of extreme values on the left side of the distribution, which can significantly affect the mean. These extreme values are often referred to as outliers, and they can have a significant impact on the statistical analysis of the data. For example, in a dataset of incomes, a few extremely low-income individuals can skew the distribution to the left, even if the majority of the population has a relatively high income.
Key Points
- A left skewed distribution has a longer tail on the left side and the majority of data points on the right side.
- The mean is typically less than the median, which is less than the mode in a left skewed distribution.
- Left skewed distributions are commonly observed in fields such as economics, finance, and social sciences.
- Outliers on the left side of the distribution can significantly affect the mean and statistical analysis of the data.
- Left skewed distributions can be modeled using various statistical distributions, such as the lognormal distribution or the Weibull distribution.
Characteristics of Left Skewed Distributions
Left skewed distributions have several distinct characteristics that set them apart from other types of distributions. One of the key characteristics is the presence of a longer tail on the left side of the distribution. This tail is often composed of a small number of extreme values that are significantly lower than the majority of the data points. Another characteristic of left skewed distributions is the fact that the mean is typically less than the median, which is less than the mode. This is in contrast to right skewed distributions, where the mean is greater than the median, which is greater than the mode.
Types of Left Skewed Distributions
There are several types of statistical distributions that can be used to model left skewed data. One of the most common is the lognormal distribution, which is often used to model income data or other types of data that are skewed to the left. Another type of distribution that can be used to model left skewed data is the Weibull distribution, which is often used to model failure times or other types of data that are skewed to the left. Other types of distributions that can be used to model left skewed data include the gamma distribution and the exponential distribution.
| Distribution | Description |
|---|---|
| Lognormal Distribution | Often used to model income data or other types of data that are skewed to the left. |
| Weibull Distribution | Often used to model failure times or other types of data that are skewed to the left. |
| Gamma Distribution | Can be used to model left skewed data, particularly in fields such as engineering and physics. |
| Exponential Distribution | Can be used to model left skewed data, particularly in fields such as reliability engineering and survival analysis. |
Real-World Applications of Left Skewed Distributions
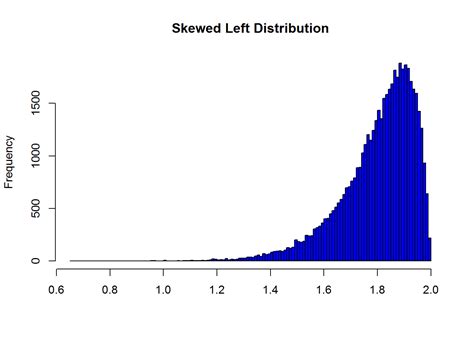
Left skewed distributions have a wide range of real-world applications, particularly in fields such as economics, finance, and social sciences. For example, income data is often left skewed, with a small number of extremely high-income individuals skewing the distribution to the right. However, when looking at the distribution of incomes below a certain threshold, the distribution can become left skewed, with a small number of extremely low-income individuals skewing the distribution to the left.
Left skewed distributions can also be observed in fields such as reliability engineering and survival analysis, where the time to failure or survival time is often left skewed. For example, the time to failure of a mechanical component may be left skewed, with a small number of components failing very early in their lifespan, while the majority of components last for a much longer period of time.
Statistical Analysis of Left Skewed Distributions
When working with left skewed distributions, it’s essential to use robust statistical methods that can handle the presence of outliers and skewness. One common approach is to use non-parametric statistical methods, such as the Wilcoxon rank-sum test or the Kruskal-Wallis test, which can provide a more robust estimate of the distribution’s parameters. Another approach is to use parametric statistical methods, such as the lognormal distribution or the Weibull distribution, which can provide a more accurate estimate of the distribution’s parameters, but require careful examination of the data for outliers and skewness.
What is the difference between a left skewed distribution and a right skewed distribution?
+A left skewed distribution has a longer tail on the left side and the majority of data points on the right side, while a right skewed distribution has a longer tail on the right side and the majority of data points on the left side.
What are some common types of statistical distributions that can be used to model left skewed data?
+Some common types of statistical distributions that can be used to model left skewed data include the lognormal distribution, the Weibull distribution, the gamma distribution, and the exponential distribution.
What are some real-world applications of left skewed distributions?
+Left skewed distributions have a wide range of real-world applications, particularly in fields such as economics, finance, and social sciences, as well as in reliability engineering and survival analysis.
Meta Description: Learn about left skewed distributions, including their characteristics, types, and real-world applications, and discover how to analyze and model left skewed data using robust statistical methods. (149 characters)