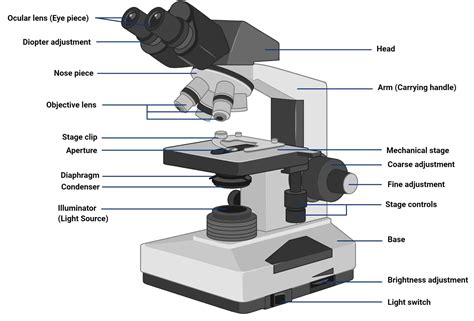
The light microscope, also known as the optical microscope, is a fundamental tool in biology, medicine, and various scientific fields. Its invention in the 16th century revolutionized the study of microorganisms, cells, and tissues, enabling scientists to explore the microscopic world in unprecedented detail. The light microscope works by using visible light to illuminate specimens, which are then magnified by a system of lenses, allowing users to observe tiny structures and details that are invisible to the naked eye.
Over the centuries, the light microscope has undergone significant improvements, with advancements in lens design, illumination systems, and microscopy techniques. Today, light microscopes are equipped with sophisticated features such as phase contrast, fluorescence, and differential interference contrast, which enhance image quality and provide valuable information about specimen morphology and behavior. The versatility and relatively low cost of light microscopes have made them an essential instrument in laboratories, educational institutions, and research facilities worldwide.
Key Points
- The light microscope uses visible light to illuminate specimens, allowing for the observation of microscopic structures and details.
- Advancements in lens design, illumination systems, and microscopy techniques have significantly improved the performance and capabilities of light microscopes.
- Light microscopes are equipped with various contrast methods, including phase contrast, fluorescence, and differential interference contrast, to enhance image quality and provide valuable information about specimen morphology and behavior.
- The versatility and relatively low cost of light microscopes have made them an essential instrument in laboratories, educational institutions, and research facilities worldwide.
- Light microscopes have a wide range of applications, including biological research, medical diagnosis, and quality control in various industries.
Principles of Light Microscopy
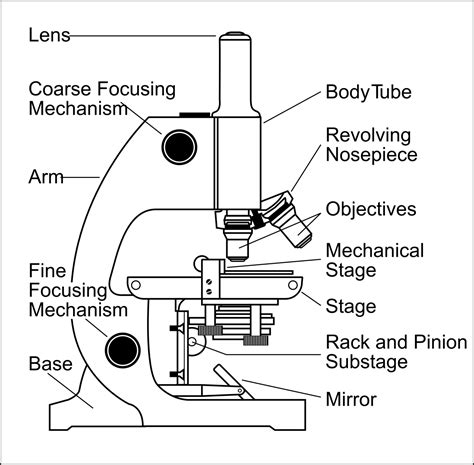
Light microscopy is based on the principle of magnification, where a system of lenses enlarges the image of a specimen, allowing users to observe tiny details that are not visible to the naked eye. The process involves several key components, including the light source, condenser, objective lenses, and eyepieces. The light source provides the illumination necessary for imaging, while the condenser focuses the light onto the specimen. The objective lenses collect the light transmitted through the specimen and magnify the image, which is then further magnified by the eyepieces.
Types of Light Microscopes
There are several types of light microscopes, each with its own unique features and applications. The most common types include brightfield microscopes, phase contrast microscopes, and fluorescence microscopes. Brightfield microscopes use visible light to illuminate specimens and are commonly used for routine laboratory work. Phase contrast microscopes use a special condenser and objective lens to enhance contrast and are often used to study living cells and microorganisms. Fluorescence microscopes use fluorescent dyes or proteins to label specific structures or molecules, allowing for high-contrast imaging and localization of specific targets.
| Type of Microscope | Description | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Brightfield Microscope | Uses visible light to illuminate specimens | Routine laboratory work, education, and research |
| Phase Contrast Microscope | Enhances contrast using special condenser and objective lens | Study of living cells and microorganisms, cell biology, and microbiology |
| Fluorescence Microscope | Uses fluorescent dyes or proteins to label specific structures or molecules | Cell biology, molecular biology, and biomedical research |

Advances in Light Microscopy

In recent years, significant advances have been made in light microscopy, including the development of super-resolution microscopy techniques, such as stimulated emission depletion (STED) and photoactivated localization microscopy (PALM). These techniques allow for imaging at resolutions below the diffraction limit, enabling researchers to study biological structures and processes at the nanoscale. Additionally, advancements in microscope design, such as the development of automated microscopes and high-throughput imaging systems, have improved the efficiency and productivity of light microscopy.
Other advances in light microscopy include the development of new contrast methods, such as structured illumination microscopy (SIM) and single-molecule localization microscopy (SMLM). These techniques provide high-contrast imaging and allow for the study of specific molecular targets, enabling researchers to gain a deeper understanding of biological processes and mechanisms. Furthermore, the integration of light microscopy with other imaging modalities, such as electron microscopy and spectroscopy, has enabled researchers to study biological systems in unprecedented detail.
Applications of Light Microscopy
Light microscopy has a wide range of applications in various fields, including biology, medicine, and materials science. In biology, light microscopy is used to study cells, tissues, and microorganisms, and to understand biological processes and mechanisms. In medicine, light microscopy is used for diagnostic purposes, such as examining tissue samples and identifying diseases. In materials science, light microscopy is used to study the properties and behavior of materials at the microscale.
In addition to its applications in research and medicine, light microscopy is also used in education and industry. In educational settings, light microscopy is used to teach students about biology, microscopy, and scientific research methods. In industry, light microscopy is used for quality control, inspection, and testing of materials and products.
What is the principle of light microscopy?
+Light microscopy is based on the principle of magnification, where a system of lenses enlarges the image of a specimen, allowing users to observe tiny details that are not visible to the naked eye.
What are the different types of light microscopes?
+There are several types of light microscopes, including brightfield microscopes, phase contrast microscopes, and fluorescence microscopes. Each type has its own unique features and applications.
What are the applications of light microscopy?
+Light microscopy has a wide range of applications in various fields, including biology, medicine, and materials science. It is used for research, diagnosis, education, and industry, and has many practical applications in everyday life.
Meta Description: Discover the principles and applications of light microscopy, a fundamental tool in biology, medicine, and scientific research. Learn about the different types of light microscopes, their features, and uses, and explore the many applications of light microscopy in various fields.