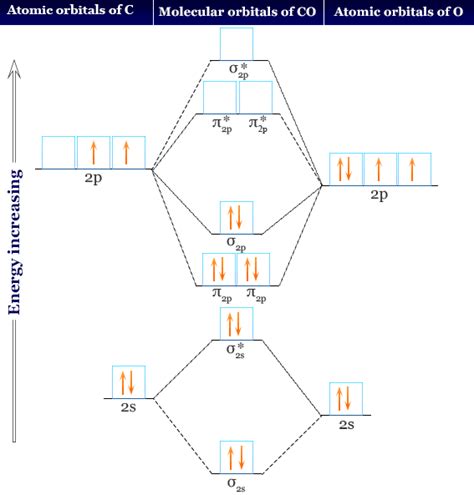
The molecular diagram of CO, also known as carbon monoxide, is a simple yet fascinating molecule that consists of one carbon atom and one oxygen atom. The molecular structure of CO is typically represented by the chemical formula CO, where the carbon atom is bonded to the oxygen atom through a triple bond. This triple bond consists of one sigma (σ) bond and two pi (π) bonds, which are formed by the overlap of the atomic orbitals of the carbon and oxygen atoms.
Chemical Structure and Bonding

The carbon atom in CO has four valence electrons, while the oxygen atom has six valence electrons. To form a stable molecule, the carbon atom shares its four valence electrons with the oxygen atom, resulting in a triple bond. The sigma bond is formed by the overlap of the carbon 2s orbital and the oxygen 2p orbital, while the two pi bonds are formed by the overlap of the carbon 2p orbitals and the oxygen 2p orbitals. This triple bond is responsible for the strong and stable nature of the CO molecule.
Molecular Orbital Diagram
A molecular orbital diagram is a useful tool for visualizing the bonding and antibonding orbitals in a molecule. The molecular orbital diagram of CO shows that the molecule has a total of six molecular orbitals: three bonding orbitals (σ, π, and π) and three antibonding orbitals (σ, π, and π*). The bonding orbitals are occupied by the valence electrons of the carbon and oxygen atoms, while the antibonding orbitals are empty. The molecular orbital diagram of CO is as follows:
| Molecular Orbital | Energy Level |
|---|---|
| σ (1s) | Lowest energy level |
| σ* (1s) | Higher energy level |
| σ (2s) | Middle energy level |
| π (2p) | Middle energy level |
| π (2p) | Middle energy level |
| σ* (2s) | Higher energy level |
| π* (2p) | Higher energy level |
| π* (2p) | Higher energy level |
Physical and Chemical Properties
The molecular diagram of CO also provides valuable information about its physical and chemical properties. CO is a colorless, odorless, and tasteless gas at room temperature and pressure. It has a molecular weight of 28.01 g/mol and a boiling point of -191.5°C. CO is highly toxic and flammable, and it is commonly used as a fuel and a reducing agent in various industrial processes.
Reactivity and Applications
CO is a highly reactive molecule that can react with a variety of substances to form a range of products. It is commonly used as a reducing agent in the production of metals, such as iron and steel, and as a fuel in the production of energy. CO is also used as a precursor to a variety of chemicals, such as methanol and formic acid. The reactivity of CO is due to the presence of the triple bond, which makes it highly susceptible to nucleophilic attack.
Key Points
- The molecular diagram of CO shows a triple bond between the carbon and oxygen atoms.
- The molecular orbital diagram of CO shows six molecular orbitals: three bonding orbitals and three antibonding orbitals.
- CO is a highly reactive molecule that can react with a variety of substances to form a range of products.
- CO is commonly used as a reducing agent and a fuel in various industrial processes.
- The physical and chemical properties of CO make it a highly useful molecule in a range of applications.
In conclusion, the molecular diagram of CO provides valuable insights into the bonding and antibonding orbitals of the molecule, as well as its physical and chemical properties. The reactivity and applications of CO make it a highly useful molecule in a range of industrial processes, and its study is essential for understanding its chemical properties and behavior.
What is the molecular structure of CO?
+The molecular structure of CO consists of one carbon atom and one oxygen atom, with a triple bond between them.
What is the molecular orbital diagram of CO?
+The molecular orbital diagram of CO shows six molecular orbitals: three bonding orbitals and three antibonding orbitals.
What are the physical and chemical properties of CO?
+CO is a colorless, odorless, and tasteless gas at room temperature and pressure, with a molecular weight of 28.01 g/mol and a boiling point of -191.5°C.
Meta Description: Learn about the molecular diagram of CO, including its chemical structure, molecular orbital diagram, physical and chemical properties, and reactivity. Understand the importance of CO in various industrial processes and its applications. (147 characters)