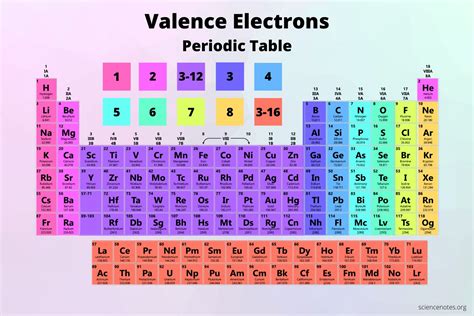
The Periodic Table of Elements is a fundamental tool in chemistry, organizing elements based on their atomic number, electron configuration, and recurring chemical properties. The valence electrons, which are the electrons in the outermost shell of an atom, play a crucial role in determining the chemical properties of an element. In this article, we will delve into the world of valence electrons and explore how they are distributed across the Periodic Table.
Understanding Valence Electrons
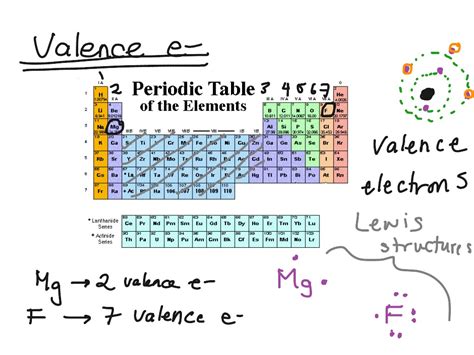
Valence electrons are the electrons in the outermost energy level of an atom, which is also known as the valence shell. The number of valence electrons an atom has determines its chemical reactivity and the types of chemical bonds it can form. Elements with a full outer energy level are stable and unreactive, while elements with partially filled outer energy levels are highly reactive.
Valence Electrons and the Periodic Table
The Periodic Table is arranged in a way that elements with the same number of valence electrons are placed in the same group (vertical column). This means that elements in the same group have similar chemical properties, as they have the same number of valence electrons. The number of valence electrons an element has can be determined by looking at its position in the Periodic Table.
| Group Number | Number of Valence Electrons |
|---|---|
| 1 (Alkali Metals) | 1 |
| 2 (Alkaline Earth Metals) | 2 |
| 13 (Boron Group) | 3 |
| 14 (Carbon Group) | 4 |
| 15 (Nitrogen Group) | 5 |
| 16 (Chalcogens) | 6 |
| 17 (Halogens) | 7 |
| 18 (Noble Gases) | 8 |
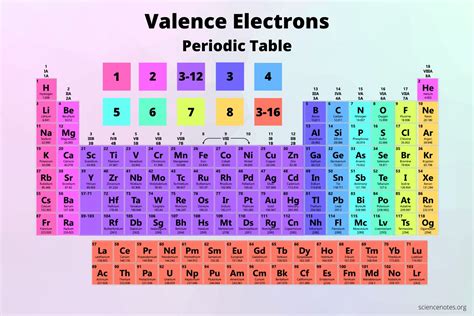
Blocks of the Periodic Table
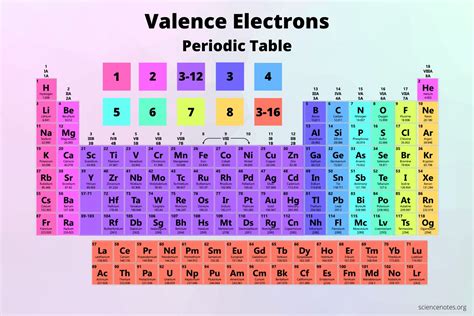
The Periodic Table can be divided into blocks based on the orbital type of the valence electrons. The s-block elements have valence electrons in the s-orbitals, the p-block elements have valence electrons in the p-orbitals, the d-block elements have valence electrons in the d-orbitals, and the f-block elements have valence electrons in the f-orbitals.
s-Block Elements
The s-block elements are located in the first two groups of the Periodic Table and have valence electrons in the s-orbitals. These elements are highly reactive and tend to lose or gain electrons to form ions with a full outer energy level.
p-Block Elements
The p-block elements are located in the right-hand side of the Periodic Table and have valence electrons in the p-orbitals. These elements can form a variety of compounds, including molecules and ions, and exhibit a range of chemical properties.
d-Block Elements
The d-block elements are located in the middle of the Periodic Table and have valence electrons in the d-orbitals. These elements are often referred to as transition metals and exhibit a range of chemical properties, including the ability to form ions with different charges.
f-Block Elements
The f-block elements are located at the bottom of the Periodic Table and have valence electrons in the f-orbitals. These elements are often referred to as lanthanides and actinides and exhibit unique chemical properties due to the presence of f-electrons.
Key Points
- The valence electrons of an element determine its chemical reactivity and the types of chemical bonds it can form.
- Elements in the same group of the Periodic Table have the same number of valence electrons and similar chemical properties.
- The number of valence electrons an element has can be determined by looking at its position in the Periodic Table.
- The s-block, p-block, d-block, and f-block elements have valence electrons in the s-orbitals, p-orbitals, d-orbitals, and f-orbitals, respectively.
- Understanding the distribution of valence electrons across the Periodic Table is crucial for predicting the chemical properties of elements and their compounds.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the valence electrons of an element play a crucial role in determining its chemical properties and reactivity. By understanding the distribution of valence electrons across the Periodic Table, chemists can predict the chemical properties of elements and their compounds. The s-block, p-block, d-block, and f-block elements have unique chemical properties due to the presence of valence electrons in different orbitals. Further research and study of the Periodic Table and valence electrons can provide valuable insights into the chemical properties of elements and their applications in various fields.
What are valence electrons and why are they important?
+Valence electrons are the electrons in the outermost energy level of an atom and play a crucial role in determining the chemical properties of an element. They are important because they determine the chemical reactivity of an element and the types of chemical bonds it can form.
How are valence electrons distributed across the Periodic Table?
+The valence electrons are distributed across the Periodic Table in a way that elements with the same number of valence electrons are placed in the same group. The number of valence electrons an element has can be determined by looking at its position in the Periodic Table.
What are the different blocks of the Periodic Table and how do they relate to valence electrons?
+The Periodic Table can be divided into blocks based on the orbital type of the valence electrons. The s-block elements have valence electrons in the s-orbitals, the p-block elements have valence electrons in the p-orbitals, the d-block elements have valence electrons in the d-orbitals, and the f-block elements have valence electrons in the f-orbitals.