Route planning is an essential aspect of logistics and navigation, especially when dealing with multiple destinations or stops. The ability to efficiently plan and optimize routes can greatly impact various industries, from delivery services to field operations and even personal travel. This article aims to delve into the intricacies of planning routes with multiple stops, exploring the challenges, strategies, and technologies involved.
Understanding the Complexity of Multi-Stop Route Planning
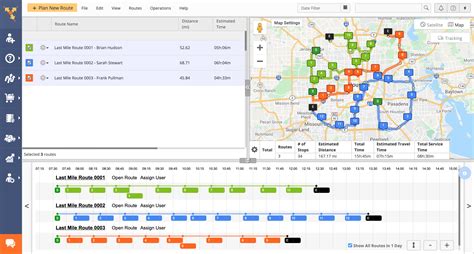
When planning routes with multiple stops, several factors come into play, making it a complex task. Unlike simple point-to-point navigation, multi-stop route planning requires considering various constraints and objectives to optimize efficiency. These constraints can include time windows for deliveries or appointments, vehicle capacity limitations, traffic conditions, and even customer preferences.
The challenge lies in finding the most efficient sequence of stops that minimizes travel time, reduces fuel consumption, and meets all the specified constraints. This is where advanced route planning algorithms and technologies become crucial.
The Role of Optimization Algorithms
Optimization algorithms are at the heart of effective multi-stop route planning. These algorithms, often based on mathematical models, aim to find the best possible solution within a given set of constraints. The most commonly used algorithm for this purpose is the Vehicle Routing Problem (VRP) algorithm, which has been extensively studied and improved upon over the years.
The VRP algorithm takes into account various parameters, such as the number of vehicles available, the capacity of each vehicle, and the distances between locations. It then generates a set of routes, ensuring that all stops are covered while minimizing the overall distance traveled. Advanced VRP algorithms can also consider time windows, allowing for more precise planning.
| VRP Algorithm Parameters | Description |
|---|---|
| Number of Vehicles | Determines the fleet size and resource allocation. |
| Vehicle Capacity | Sets the maximum load or passenger capacity for each vehicle. |
| Distance Matrix | Represents the distances between all pairs of locations. |
| Time Windows | Specifies the time periods when deliveries or services can be made at each stop. |
Dynamic Routing and Real-Time Adjustments
In real-world scenarios, route planning is not always a static process. Unforeseen events, such as traffic delays, road closures, or last-minute customer requests, can disrupt initially optimized routes. This is where dynamic routing comes into play.
Dynamic routing algorithms continuously monitor the progress of vehicles and adjust routes in real-time. They use real-time data from GPS tracking systems, traffic monitoring services, and customer feedback to make informed decisions. This ensures that routes remain efficient even in changing conditions.
Technological Innovations in Multi-Stop Route Planning

The field of multi-stop route planning has witnessed significant advancements thanks to technological innovations. These technologies enhance the accuracy, efficiency, and adaptability of route planning systems.
GPS and Location-Based Services
Global Positioning System (GPS) technology has revolutionized route planning. GPS devices and location-based services provide accurate real-time location data, enabling precise tracking of vehicles and stops. This data is crucial for both initial route planning and dynamic adjustments.
Furthermore, location-based services can integrate with mapping platforms, providing detailed information about road networks, traffic conditions, and even real-time incidents. This data enriches the route planning process, allowing for more informed decisions.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) techniques have been applied to multi-stop route planning to enhance optimization and decision-making. AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data, including historical route information, traffic patterns, and customer behavior, to identify trends and patterns.
ML algorithms, trained on historical data, can predict travel times, optimize route sequences, and even anticipate potential issues. For example, an AI-powered system might predict a traffic jam ahead and suggest an alternative route, ensuring timely deliveries.
Cloud Computing and Data Analytics
Cloud computing and data analytics platforms provide the computational power and storage needed to handle complex route planning tasks. These platforms allow for the efficient processing of large datasets, enabling real-time analysis and optimization.
By leveraging cloud-based route planning systems, businesses can access powerful optimization algorithms and analytical tools without the need for extensive on-premise infrastructure. This scalability and flexibility are particularly beneficial for enterprises with dynamic and expanding operations.
Case Studies: Real-World Applications of Multi-Stop Route Planning
Multi-stop route planning finds applications in various industries, each with its unique challenges and requirements. Let’s explore some real-world case studies to understand the practical implications of effective route planning.
Delivery Services and Logistics
The logistics and delivery industry heavily relies on efficient route planning to optimize delivery routes and reduce costs. Companies like FedEx, UPS, and Amazon utilize advanced route planning systems to manage their vast fleets and ensure timely deliveries.
For example, Amazon uses a combination of AI, machine learning, and real-time data to optimize delivery routes. Their system considers factors such as package weight, delivery addresses, and traffic conditions to create the most efficient routes for their delivery drivers.
Field Service Operations
Field service operations, such as maintenance and repair services, benefit greatly from multi-stop route planning. Technicians often need to visit multiple customer sites in a day, and efficient route planning ensures they can complete more jobs in less time.
A field service company, ProServe, utilizes a dynamic route planning system that considers the locations of customer sites, the skills and availability of technicians, and even the type of equipment required for each job. This ensures that the right technician is dispatched to the right location, minimizing travel time and maximizing productivity.
Last-Mile Delivery and E-commerce
With the rise of e-commerce, last-mile delivery has become a critical aspect of online retail. Efficient route planning is essential to ensure timely and cost-effective deliveries to customers’ doorsteps.
An e-commerce company, eShop, has implemented a multi-stop route planning system that considers the density of delivery areas, the capacity of delivery vehicles, and customer preferences. This system optimizes routes, reducing the number of vehicles required and improving the overall customer experience.
Future Trends and Innovations
The field of multi-stop route planning continues to evolve, driven by advancements in technology and changing industry needs. Here are some future trends and innovations to watch out for:
Autonomous Vehicles and Drones
The integration of autonomous vehicles and drones into delivery fleets is expected to revolutionize multi-stop route planning. These technologies offer increased efficiency, reduced labor costs, and the potential for 24⁄7 operations.
Autonomous vehicles can navigate complex routes, making multiple stops without the need for a human driver. Drones, with their ability to cover short distances quickly, can be used for last-mile deliveries, further optimizing the overall delivery process.
Predictive Analytics and Forecasting
Predictive analytics and forecasting techniques will play a significant role in future route planning. By analyzing historical data and patterns, systems can predict future demand, traffic conditions, and even customer behavior, allowing for more accurate route planning and resource allocation.
Collaborative Route Planning
Collaborative route planning involves optimizing routes for multiple vehicles or fleets. This approach is particularly beneficial for industries where multiple entities share the same road network, such as urban delivery services or public transportation.
By collaborating and sharing real-time data, these entities can optimize routes collectively, reducing congestion and improving overall efficiency. This collaborative approach requires advanced coordination and communication systems.
Green Route Planning
With growing environmental concerns, green route planning is gaining importance. This approach aims to minimize the environmental impact of transportation by optimizing routes to reduce fuel consumption and emissions.
Green route planning considers factors such as vehicle fuel efficiency, traffic conditions, and even the layout of the road network to find the most eco-friendly routes. This not only benefits the environment but also reduces operational costs for businesses.
Conclusion

Planning routes with multiple stops is a complex yet critical task that impacts various industries. By leveraging advanced optimization algorithms, real-time data, and technological innovations, businesses can enhance their operational efficiency, reduce costs, and improve customer satisfaction.
As technology continues to advance, the future of multi-stop route planning looks promising. With the integration of autonomous vehicles, predictive analytics, and collaborative systems, route planning will become even more efficient and sustainable. Stay tuned for the next wave of innovations in this exciting field!
How can businesses optimize their multi-stop routes to reduce costs and improve efficiency?
+Businesses can employ advanced route planning algorithms, such as the Vehicle Routing Problem (VRP) algorithm, to optimize their multi-stop routes. These algorithms consider factors like vehicle capacity, distances between locations, and time windows to find the most efficient route. Additionally, real-time data from GPS and traffic monitoring can be used for dynamic adjustments, ensuring routes remain optimal despite changing conditions.
What are the benefits of using AI and machine learning in multi-stop route planning?
+AI and machine learning bring several advantages to multi-stop route planning. They can analyze vast amounts of data, including historical routes, traffic patterns, and customer behavior, to predict travel times and optimize routes. This allows for more accurate and efficient decision-making, reducing costs and improving overall productivity.
How can collaborative route planning benefit urban delivery services and public transportation?
+Collaborative route planning involves optimizing routes for multiple vehicles or fleets, taking into account real-time data and coordination. This approach is beneficial for urban delivery services and public transportation as it reduces congestion, improves efficiency, and enhances overall network performance. By sharing data and collaborating, these entities can collectively find the most optimal routes, benefiting both operators and customers.



