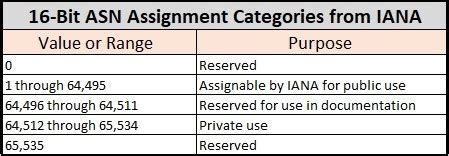
Private BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) Autonomous System Numbers (ASNs) are a set of numbers reserved for private use, similar to private IP addresses. These numbers are not routable on the internet and are used for internal routing or testing purposes within organizations. The use of private ASNs is defined in the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) document RFC 6996, which replaced the earlier RFC 4893 and RFC 5398 for 16-bit and 32-bit ASNs, respectively. The current RFCs governing ASNs are based on the understanding that the number of available public ASNs is limited, and their conservation is important for the sustainability of the internet's routing infrastructure.
Private BGP AS Number Ranges
The private ASNs are divided into two ranges for 16-bit and 32-bit ASNs. For 16-bit ASNs, the private range is from 64512 to 65534, inclusive. This range allows for 1023 private ASNs (65534 - 64512 + 1 = 1023). For 32-bit ASNs, the private range is from 4200000000 to 4294967294, with the range from 65536 to 4199999999 being reserved for future use, and the range from 4294967295 to 4294967295 being reserved.
Using Private BGP AS Numbers
Private BGP ASNs are used in scenarios where an organization does not need to be uniquely identified on the global internet. This could be within a private network, for testing purposes, or when an organization does not plan to peer with other autonomous systems directly. However, it’s crucial to ensure that these private ASNs do not leak into the global BGP routing tables, as this could cause routing conflicts or blackholing of traffic. Network administrators should take precautions, such as filtering private ASNs at network borders, to prevent such occurrences.
| ASN Type | Private Range |
|---|---|
| 16-bit ASNs | 64512 to 65534 |
| 32-bit ASNs | 4200000000 to 4294967294 |
Examples of Private BGP AS Numbers

Here are 5 examples of private BGP AS numbers that fall within the defined ranges:
- 64512: This is the first private ASN in the 16-bit range and can be used for internal network testing or organization.
- 4200000000: This is the first private ASN in the 32-bit range and is suitable for large, complex networks that require more unique identifiers.
- 65534: This is the last private ASN in the 16-bit range and might be used in scenarios requiring isolation from other parts of the network.
- 4294967294: This is the last private ASN in the 32-bit range and represents the upper limit of private ASNs available for use.
- 65001: While not mentioned in the initial range explanation, ASNs like 65001 are within the private range (64512 to 65534) and can be utilized for various internal networking purposes, providing flexibility in network design.
Best Practices for Private ASNs
When utilizing private BGP ASNs, it’s essential to follow best practices to avoid potential issues. This includes configuring BGP to filter out private ASNs from being advertised to the internet, using them consistently within the organization’s network to avoid confusion, and documenting their use for future reference and troubleshooting purposes.
Key Points
- Private BGP ASNs are used for internal routing and testing purposes.
- The 16-bit private ASN range is from 64512 to 65534.
- The 32-bit private ASN range is from 4200000000 to 4294967294.
- Proper configuration and filtering are crucial to prevent private ASNs from leaking into the global internet.
- Documentation and consistent use of private ASNs are key to maintaining network integrity and facilitating troubleshooting.
In conclusion, private BGP AS numbers provide a valuable tool for network administrators to manage internal network routing without the need for unique public ASNs. Understanding their proper use, configuration, and the importance of preventing their leakage into the global internet is crucial for maintaining network stability and security.
What is the purpose of private BGP AS numbers?
+Private BGP AS numbers are used for internal routing and testing purposes within organizations, allowing for network isolation and flexibility without the need for globally unique ASNs.
How do I prevent private ASNs from leaking into the global internet?
+Preventing private ASNs from leaking into the global internet can be achieved by configuring BGP to filter out private ASNs from being advertised to the internet. This is typically done through the use of route maps and prefix lists that deny the advertisement of private ASNs.
What are the consequences of private ASNs leaking into the global internet?
+The leakage of private ASNs into the global internet can cause routing conflicts or blackholing of traffic. This is because private ASNs are not unique and can be used by multiple organizations, leading to ambiguity in routing decisions.