Steel, a fundamental material in modern construction and manufacturing, is an alloy primarily composed of iron and carbon. The chemical formula for steel is not as straightforward as other compounds due to its alloy nature, which means it is a mixture of different elements. However, the basic chemical formula for steel can be represented as Fe-C, indicating it is mostly iron (Fe) with a carbon (C) content that can vary significantly. The carbon content in steel can range from less than 0.1% to over 2.1%, which drastically affects its properties, such as strength, ductility, and hardness.
Understanding Steel Composition
Steel’s composition is not limited to just iron and carbon. It can contain a variety of other elements, including manganese, chromium, vanadium, and nickel, among others. These elements are added to enhance specific properties of the steel, such as corrosion resistance, strength at high temperatures, and formability. For instance, stainless steel, which contains a minimum of 10.5% chromium, is highly resistant to corrosion and is widely used in kitchen utensils, surgical equipment, and construction.
Chemical Composition Variations
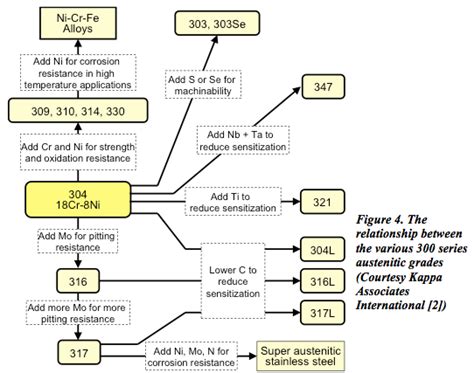
The chemical composition of steel can be highly variable, leading to different types of steel, each with its unique properties and applications. For example, carbon steel, which contains up to 2.1% carbon, is further divided into low-carbon steel (less than 0.3% carbon), medium-carbon steel (0.3-0.6% carbon), and high-carbon steel (0.6-2.1% carbon). Alloy steels contain additional elements like manganese, silicon, nickel, and chromium in specific proportions to achieve desired properties.
| Steel Type | Carbon Content | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Low-Carbon Steel | Less than 0.3% | Ductile, easy to form, used in wires, pipes |
| Medium-Carbon Steel | 0.3-0.6% | Balances strength and ductility, used in automotive parts |
| High-Carbon Steel | 0.6-2.1% | Hard, strong, used in cutting tools, springs |
Steel Production Process

The production of steel involves several steps, starting from the extraction of iron ore and coal, followed by their processing into pig iron, which is then further refined to produce steel. This process can involve basic oxygen steelmaking, electric arc furnace steelmaking, or other methods, each with its advantages and specific applications. The steel production process also involves the addition of various alloying elements to achieve the desired chemical composition and properties.
Importance of Chemical Formula in Steel Applications
Understanding the chemical formula and composition of steel is vital for its application in various industries. For instance, in construction, the choice between different steel alloys can affect the strength, durability, and sustainability of buildings. Similarly, in automotive manufacturing, the selection of steel with the appropriate chemical composition can influence vehicle safety, fuel efficiency, and overall performance.
Key Points
- The chemical formula for steel is primarily represented as Fe-C, with iron being the main component and carbon content varying.
- Steel composition can include a variety of elements beyond iron and carbon, such as manganese, chromium, and nickel, to enhance its properties.
- Different types of steel, including carbon steel and alloy steel, have distinct applications based on their chemical composition and resulting properties.
- The production of steel involves refining iron ore and coal into pig iron and then into steel, with the addition of alloying elements to achieve the desired properties.
- Understanding the chemical composition of steel is crucial for optimizing its performance, safety, and cost-effectiveness in various industries.
In conclusion, the chemical formula of steel, while fundamentally based on iron and carbon, encompasses a broad range of compositions and properties. This versatility makes steel a cornerstone material in modern technology and industry, with its applications spanning from simple tools to complex infrastructure and machinery.
What is the primary component of steel?
+Iron (Fe) is the primary component of steel, with carbon (C) being a significant secondary component that affects its properties.
How does the carbon content affect steel properties?
+The carbon content in steel can significantly affect its strength, hardness, and ductility. Low-carbon steel is more ductile, while high-carbon steel is harder and stronger.
What are some common applications of steel based on its chemical composition?
+Steel is used in construction for its strength and durability, in automotive manufacturing for its balance of strength and formability, and in cutlery and surgical equipment for its hardness and resistance to corrosion.
