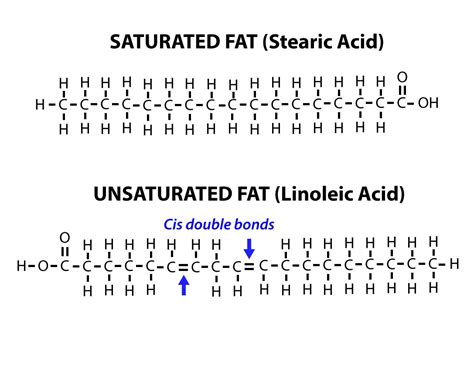
Unsaturated fatty acids are a type of dietary fat that play a crucial role in maintaining various bodily functions, including heart health, brain function, and the absorption of essential vitamins. Unlike saturated fats, which have single bonds between the carbon atoms of the fatty acid chain, unsaturated fats have one or more double bonds. This distinction in molecular structure gives unsaturated fatty acids their unique properties and health benefits. The presence of double bonds in unsaturated fatty acids makes them more flexible and liquid at room temperature, which is why they are often found in higher amounts in plant-based foods and fatty fish.
The classification of unsaturated fatty acids is based on the number and position of the double bonds. Monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFAs) have one double bond, while polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) have multiple double bonds. Both types of unsaturated fats are essential for human health, but they cannot be produced by the body and must be obtained through the diet. Examples of monounsaturated fats include oleic acid, found in olive oil, and palmitoleic acid, found in macadamia nuts. Polyunsaturated fats are further divided into omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, with examples including alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) from flaxseeds and eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) from fatty fish.
Key Points
- Unsaturated fatty acids are crucial for heart health, brain function, and vitamin absorption.
- Monounsaturated fatty acids have one double bond, while polyunsaturated fatty acids have multiple double bonds.
- Omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids are types of polyunsaturated fats with distinct health benefits.
- Unsaturated fats are found in higher amounts in plant-based foods and fatty fish.
- A balanced diet that includes sources of unsaturated fats is essential for maintaining overall health.
Health Benefits of Unsaturated Fatty Acids

Consuming unsaturated fatty acids as part of a balanced diet has been associated with several health benefits. One of the primary advantages of unsaturated fats is their ability to help lower levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, often referred to as “bad” cholesterol, which can reduce the risk of heart disease. Additionally, unsaturated fats, particularly omega-3 fatty acids, have anti-inflammatory properties that may help in managing conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis and may also play a role in cognitive function and depression management.
Role in Heart Health
The impact of unsaturated fatty acids on heart health is a well-studied area. By replacing saturated fats with unsaturated fats in the diet, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of heart disease. This is because unsaturated fats help in reducing the levels of triglycerides and LDL cholesterol, both of which are risk factors for heart disease. Furthermore, the inclusion of omega-3 fatty acids, particularly EPA and DHA, has been shown to lower the risk of heart disease due to their effects on blood lipid profiles, blood pressure, and the prevention of blood clots.
| Fatty Acid Type | Food Sources | Health Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Monounsaturated Fats | Olive oil, avocados, nuts | Lower LDL cholesterol, improve heart health |
| Polyunsaturated Fats (Omega-3) | Fatty fish, flaxseeds, chia seeds | Reduce inflammation, improve heart health, support brain function |
| Polyunsaturated Fats (Omega-6) | Soybean oil, corn oil, sunflower oil | Support heart health, but balance with omega-3 is crucial |

Dietary Recommendations and Sources

The dietary guidelines recommend that adults limit their intake of saturated fats and instead choose foods rich in unsaturated fats. For a healthy diet, it is suggested to consume 20-35% of total daily calories from fat, with an emphasis on unsaturated fats. Monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats can be found in a variety of foods, including vegetable oils (such as olive, canola, and soybean oil), nuts and seeds (like almonds, walnuts, flaxseeds, and chia seeds), fatty fish (such as salmon, mackerel, and sardines), and avocados.
Navigating Food Labels
When navigating food labels, it’s essential to look beyond the total fat content and examine the types of fat present. Foods high in unsaturated fats and low in saturated and trans fats are generally healthier choices. However, it’s also important to consider the overall nutrient profile of the food, including its content of vitamins, minerals, and fiber, to make informed dietary decisions.
What are the primary sources of unsaturated fatty acids in the diet?
+The primary sources of unsaturated fatty acids include vegetable oils like olive oil, nuts and seeds such as almonds and flaxseeds, fatty fish like salmon, and avocados.
How do unsaturated fatty acids contribute to heart health?
+Unsaturated fatty acids help lower the levels of LDL cholesterol and triglycerides, reduce inflammation, and prevent blood clots, all of which contribute to a reduced risk of heart disease.
What is the recommended daily intake of unsaturated fats?
+The dietary guidelines suggest that 20-35% of total daily calories should come from fat, with an emphasis on unsaturated fats. However, specific recommendations can vary based on individual health needs and dietary patterns.
In conclusion, unsaturated fatty acids are a vital component of a healthy diet, offering numerous benefits for heart health, cognitive function, and the management of chronic diseases. By understanding the different types of unsaturated fats, their food sources, and how to incorporate them into a balanced diet, individuals can make informed choices to support their overall health and well-being. As with any dietary recommendation, it’s essential to consider individual needs and health status, and to consult with a healthcare provider or a registered dietitian for personalized advice.