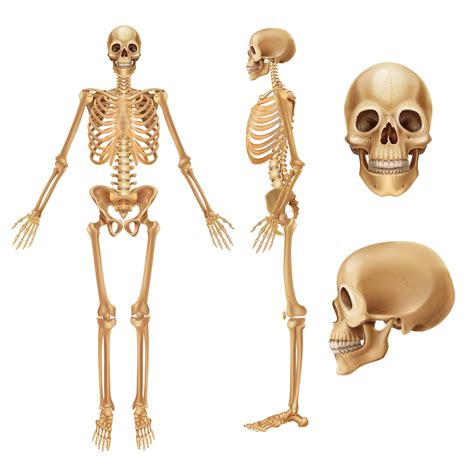
The skeletal system, also known as the musculoskeletal system, is a complex network of bones, cartilage, and ligaments that provide support, protection, and movement to the human body. A side view anatomy guide of the skeletal system is essential for understanding the relationships between different bones and their functions. In this article, we will delve into the anatomy of the skeletal system from a side view perspective, exploring the various bones, joints, and ligaments that make up this intricate system.
Key Points
- The skeletal system consists of 206 bones that provide support, protection, and movement to the body.
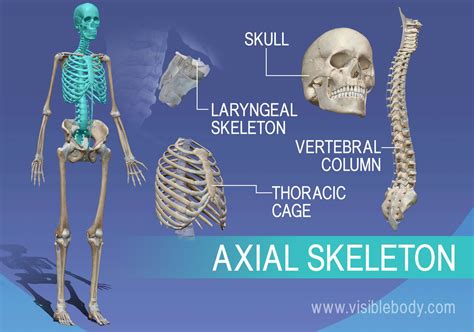
- The axial skeleton includes the skull, vertebral column, ribcage, and sternum, while the appendicular skeleton comprises the upper and lower limbs.
- The skeletal system is divided into two main categories: the axial skeleton and the appendicular skeleton.
- Joints and ligaments play a crucial role in facilitating movement and providing stability to the skeletal system.
- Understanding the anatomy of the skeletal system is essential for diagnosing and treating various musculoskeletal disorders.
Introduction to the Skeletal System
The skeletal system is a vital component of the human body, providing a framework for movement, support, and protection. From a side view perspective, the skeletal system can be divided into two main categories: the axial skeleton and the appendicular skeleton. The axial skeleton includes the bones of the skull, vertebral column, ribcage, and sternum, while the appendicular skeleton comprises the bones of the upper and lower limbs.
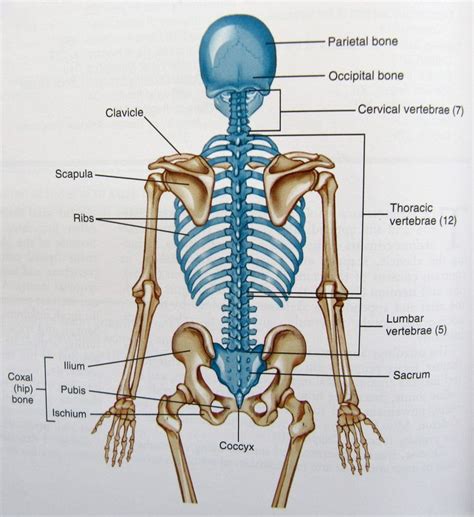
Axial Skeleton
The axial skeleton is the central part of the skeletal system, providing support and protection to the body’s vital organs. The skull, also known as the cranium, is the bony structure that encloses and protects the brain. The vertebral column, also known as the spine, is a flexible rod-like structure that extends from the base of the skull to the tailbone. The ribcage, composed of 24 ribs, provides protection to the heart and lungs, while the sternum, or breastbone, serves as the anchor point for the ribs.
Appendicular Skeleton
The appendicular skeleton, on the other hand, is responsible for facilitating movement and providing support to the body’s limbs. The upper limb consists of the scapula (shoulder blade), humerus (upper arm bone), radius and ulna (forearm bones), and the carpals, metacarpals, and phalanges (wrist and finger bones). The lower limb comprises the pelvis, femur (thigh bone), patella (kneecap), tibia and fibula (lower leg bones), and the tarsals, metatarsals, and phalanges (ankle and toe bones).
| Bone | Function |
|---|---|
| Skull | Protects the brain |
| Vertebral column | Provides support and flexibility to the body |
| Ribcage | Protects the heart and lungs |
| Scapula | Provides attachment point for muscles of the upper limb |
| Femur | Supports the body's weight and facilitates movement |
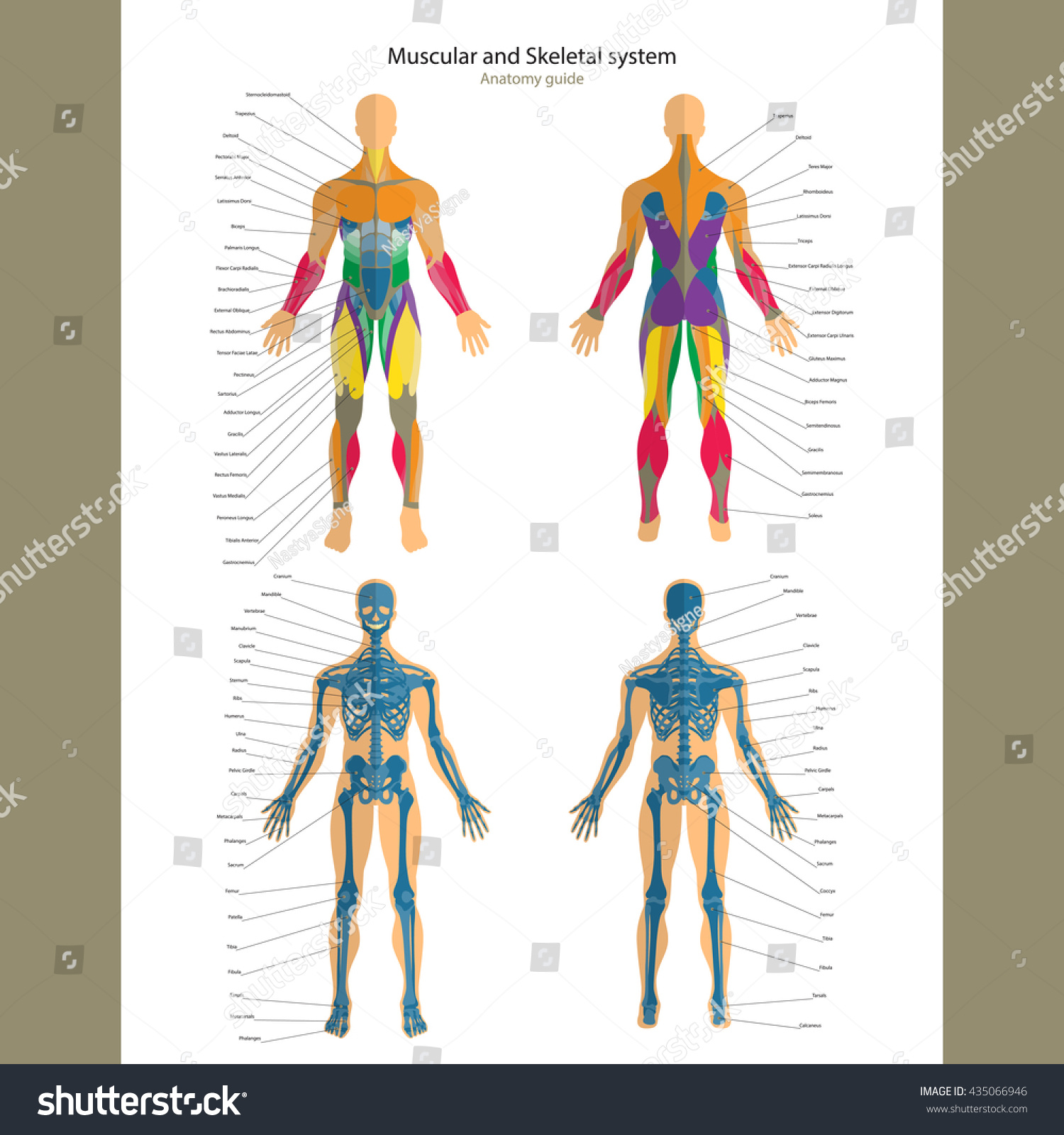
Joints and Ligaments
Joints and ligaments play a vital role in facilitating movement and providing stability to the skeletal system. Joints are the points where two or more bones meet, allowing for movement and flexibility. Ligaments, on the other hand, are fibrous connective tissues that connect bones to each other, providing support and stability to the joints. The skeletal system contains various types of joints, including ball-and-socket joints, hinge joints, and pivot joints, each with its unique characteristics and functions.
Types of Joints
Ball-and-socket joints, such as the shoulder and hip joints, allow for a wide range of motion in three planes. Hinge joints, like the elbow and knee joints, permit movement in one plane, while pivot joints, such as the atlanto-axial joint in the neck, allow for rotational movement. Understanding the different types of joints and their functions is essential for appreciating the complexity and beauty of the skeletal system.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the skeletal system is a complex and fascinating system that provides support, protection, and movement to the human body. A side view anatomy guide of the skeletal system reveals the intricate relationships between different bones, joints, and ligaments. By understanding the anatomy of the skeletal system, healthcare professionals can better diagnose and treat various musculoskeletal disorders, ultimately improving patient outcomes and quality of life.
What is the primary function of the skeletal system?
+The primary function of the skeletal system is to provide support, protection, and movement to the body.
What are the two main categories of the skeletal system?
+The two main categories of the skeletal system are the axial skeleton and the appendicular skeleton.
What is the function of ligaments in the skeletal system?
+Ligaments connect bones to each other, providing support and stability to the joints.
Meta Description: Explore the anatomy of the skeletal system from a side view perspective, including the axial and appendicular skeletons, joints, and ligaments. Understand the functions and relationships between different bones and their importance in providing support, protection, and movement to the body.