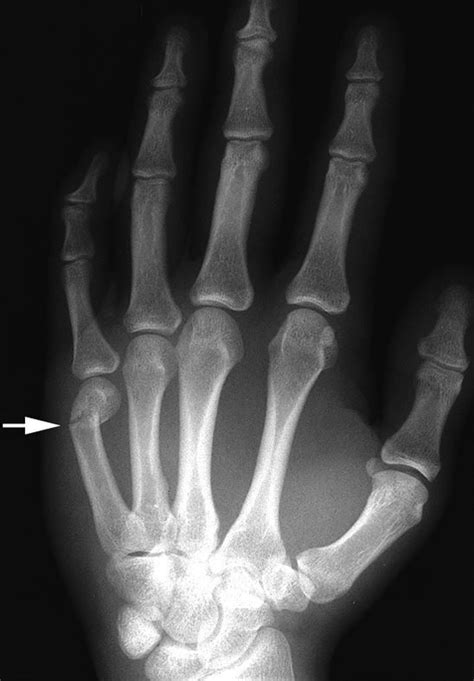
Xray hand fractures refer to the use of radiographic imaging, specifically X-rays, to diagnose and assess fractures in the hand. The hand is a complex and delicate structure, comprising 27 bones, 29 joints, and a multitude of ligaments, tendons, and muscles. Due to its intricate anatomy and frequent use, the hand is prone to various types of injuries, including fractures. X-ray technology plays a crucial role in the diagnosis and management of hand fractures, allowing healthcare professionals to visualize the internal structure of the hand and identify any abnormalities or disruptions in the bone alignment.
The process of evaluating an X-ray for a hand fracture involves a thorough examination of the radiographic images to identify any signs of fracture, such as discontinuity of the bone cortex, displacement of bone fragments, or abnormal angulation of the bones. The interpretation of X-ray images requires a high degree of expertise, as the complex anatomy of the hand can make it challenging to distinguish between normal variants and pathological conditions. Furthermore, the clinical presentation of the patient, including symptoms such as pain, swelling, and limited mobility, must be correlated with the radiographic findings to ensure an accurate diagnosis.
Key Points
- X-ray is a crucial diagnostic tool for evaluating hand fractures, allowing for the visualization of bone alignment and identification of abnormalities.
- The interpretation of X-ray images requires expertise in radiology and a thorough understanding of hand anatomy.
- Clinical correlation is essential for accurate diagnosis, as radiographic findings must be considered in conjunction with patient symptoms and physical examination results.
- There are various types of hand fractures, including phalangeal, metacarpal, and carpal fractures, each with distinct radiographic characteristics and treatment approaches.
- Timely and accurate diagnosis of hand fractures is critical for ensuring optimal treatment outcomes and preventing long-term complications, such as arthritis, stiffness, or chronic pain.
Types of Hand Fractures
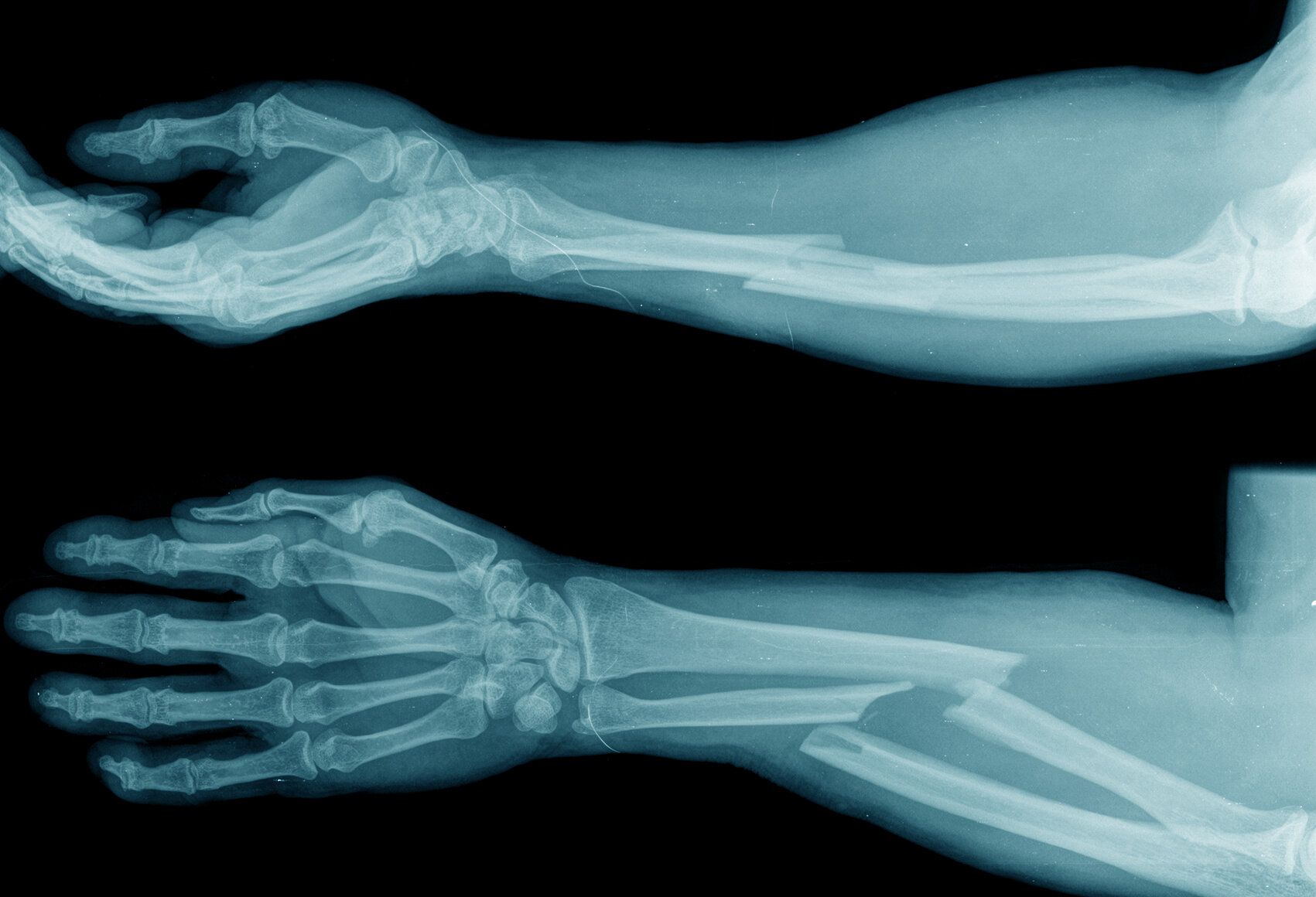
Hand fractures can be classified into several categories based on the location and type of fracture. Phalangeal fractures involve the bones of the fingers (phalanges), while metacarpal fractures affect the bones of the hand (metacarpals). Carpal fractures, on the other hand, involve the bones of the wrist (carpals). Each type of fracture has distinct radiographic characteristics and treatment approaches. For example, phalangeal fractures may require immobilization in a splint or cast, while metacarpal fractures may necessitate surgical intervention to restore proper alignment and promote healing.
Phalangeal Fractures
Phalangeal fractures are the most common type of hand fracture, accounting for approximately 40% of all hand fractures. These fractures can be further subdivided into subtypes based on the location and severity of the fracture. For instance, a fracture of the distal phalanx (the bone at the tip of the finger) may be treated conservatively with immobilization and pain management, while a fracture of the proximal phalanx (the bone at the base of the finger) may require surgical intervention to restore proper alignment and promote healing.
| Fracture Type | Location | Treatment Approach |
|---|---|---|
| Phalangeal fracture | Fingers (phalanges) | Immobilization, surgical intervention |
| Metacarpal fracture | Hand (metacarpals) | Surgical intervention, immobilization |
| Carpal fracture | Wrist (carpals) | Surgical intervention, immobilization |
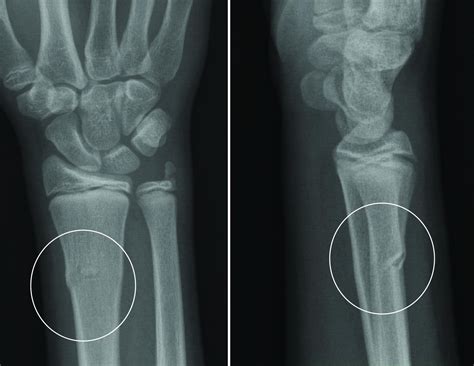
Treatment and Management
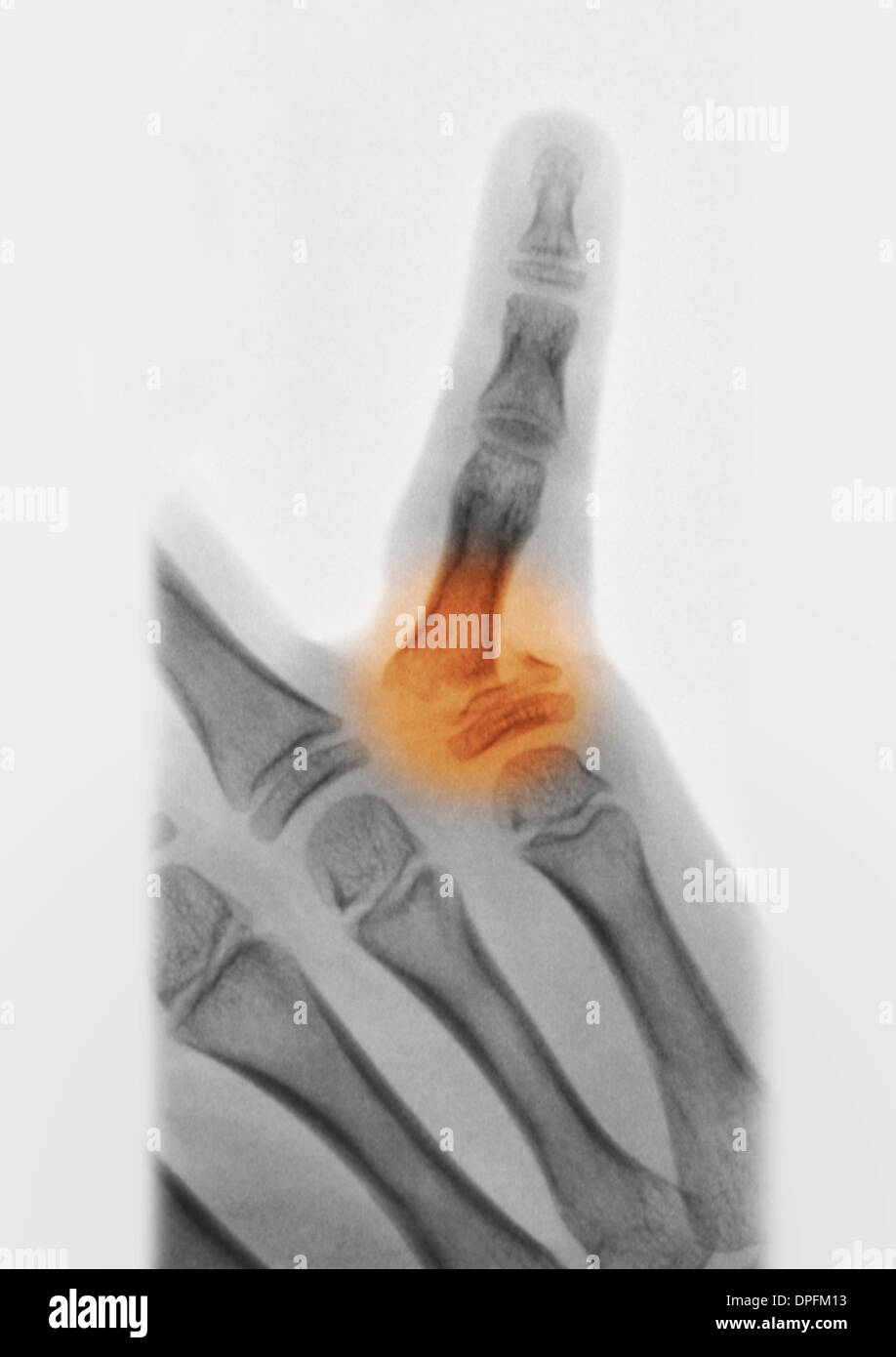
The treatment and management of hand fractures depend on the type and severity of the fracture, as well as the patient’s overall health and medical history. Conservative treatment approaches, such as immobilization in a splint or cast, may be sufficient for certain types of fractures, while others may require surgical intervention to restore proper alignment and promote healing. In some cases, a combination of conservative and surgical treatments may be necessary to achieve optimal results.
Surgical treatment of hand fractures typically involves the use of internal fixation devices, such as plates, screws, or wires, to stabilize the bone fragments and promote healing. The choice of surgical technique depends on the type and location of the fracture, as well as the patient's individual needs and preferences. In some cases, arthroscopic surgery may be used to visualize the fracture and facilitate the placement of internal fixation devices.
Complications and Long-term Outcomes
Despite advances in diagnostic and treatment approaches, hand fractures can be associated with various complications and long-term outcomes. These may include arthritis, stiffness, chronic pain, or limited mobility, among others. The risk of complications can be minimized by ensuring timely and accurate diagnosis, as well as appropriate treatment and management. Additionally, patient education and rehabilitation programs can help to promote optimal recovery and prevent long-term disability.
What are the common symptoms of a hand fracture?
+Common symptoms of a hand fracture include pain, swelling, bruising, and limited mobility. In some cases, patients may experience numbness, tingling, or weakness in the affected hand or fingers.
How are hand fractures diagnosed?
+Hand fractures are typically diagnosed using X-ray technology, which allows healthcare professionals to visualize the internal structure of the hand and identify any abnormalities or disruptions in the bone alignment.
What are the treatment options for hand fractures?
+Treatment options for hand fractures depend on the type and severity of the fracture, as well as the patient's overall health and medical history. Conservative treatment approaches, such as immobilization in a splint or cast, may be sufficient for certain types of fractures, while others may require surgical intervention to restore proper alignment and promote healing.
In conclusion, X-ray hand fractures are a common and complex condition that requires a multidisciplinary approach to diagnosis and treatment. A thorough understanding of hand anatomy, combined with expertise in radiographic interpretation and surgical techniques, is essential for ensuring optimal treatment outcomes and preventing long-term complications. By providing accurate and timely diagnosis, as well as appropriate treatment and management, healthcare professionals can help patients to recover from hand fractures and regain optimal function and mobility.